
During the preparation of final accounts, debts written off after the trial balance is finalized are transferred to the profit and loss account. “Purchases account” is also debited (equal to the amount of purchase), however, it is not necessary to show that in the above practice example. Carriage inwards is treated as a direct operating expense since the product is intended for operational use. The following section provides a brief overview and explanation of the most commonly used accounts and their types.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
These three elements are reported on the statement of financial position or balance sheet. Multiple types of companies like International Public companies, International Financial Reporting, and others are all related to GAAP. The methodologies that the executives can follow are Cash Basis, Accrual Basis, and the hybrid between the two.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
The balance in capital account increases with the introduction of new capital and profits earned by the business and decreases as a result of withdrawals and losses sustained by the business. In accounting, the accounts are classified using one of two approaches – modern approach or traditional approach. We shall describe modern approach first because this approach of classification of accounts is used in almost every advanced country. The use of traditional approach is very limited and it will be discussed later. Some accounts are used to offset other accounts known as contra accounts.
Control Accounts and Subsidiary Ledgers
If, say, you don’t own any buildings but plan to buy one next year, it’s worth including that asset class in the chart. If your business provides services and has no inventory, there’s no point to including an inventory classification in the chart, for instance. If you have accounts that include only small amounts, see if you can roll them into other account classes. It helps management to determine the cost involved in manufacturing a product or services by use of different cost accounting method.
- These classifications help students to cover the area adequately and learn the concepts clearly.
- Now that you know how accounts and sub-accounts work, you can make the necessary adjustments to your company’s bookkeeping.
- First, the executives access the information of financial accounting followed by the cost accounting.
- The classification of accounts is an essential part of bookkeeping and financial reporting.
Before we can start classifying and recording transactions, we need to understand the Accounting Equation. Examples of Nominal accounts include Sales Revenue, Service Revenue, Cost of Goods Sold, Salaries and Wages, Rent Expense, Depreciation Expense, Interest Revenue, Interest Expense, etc. Examples of Real accounts include Cash, Accounts Receivable, Inventory, Land, Buildings, Machinery, Patents, etc. 9,500 received in cash from Unreal Co. as the full and final settlement of their account worth 10,000.
Classification of Accounts in Bookkeeping
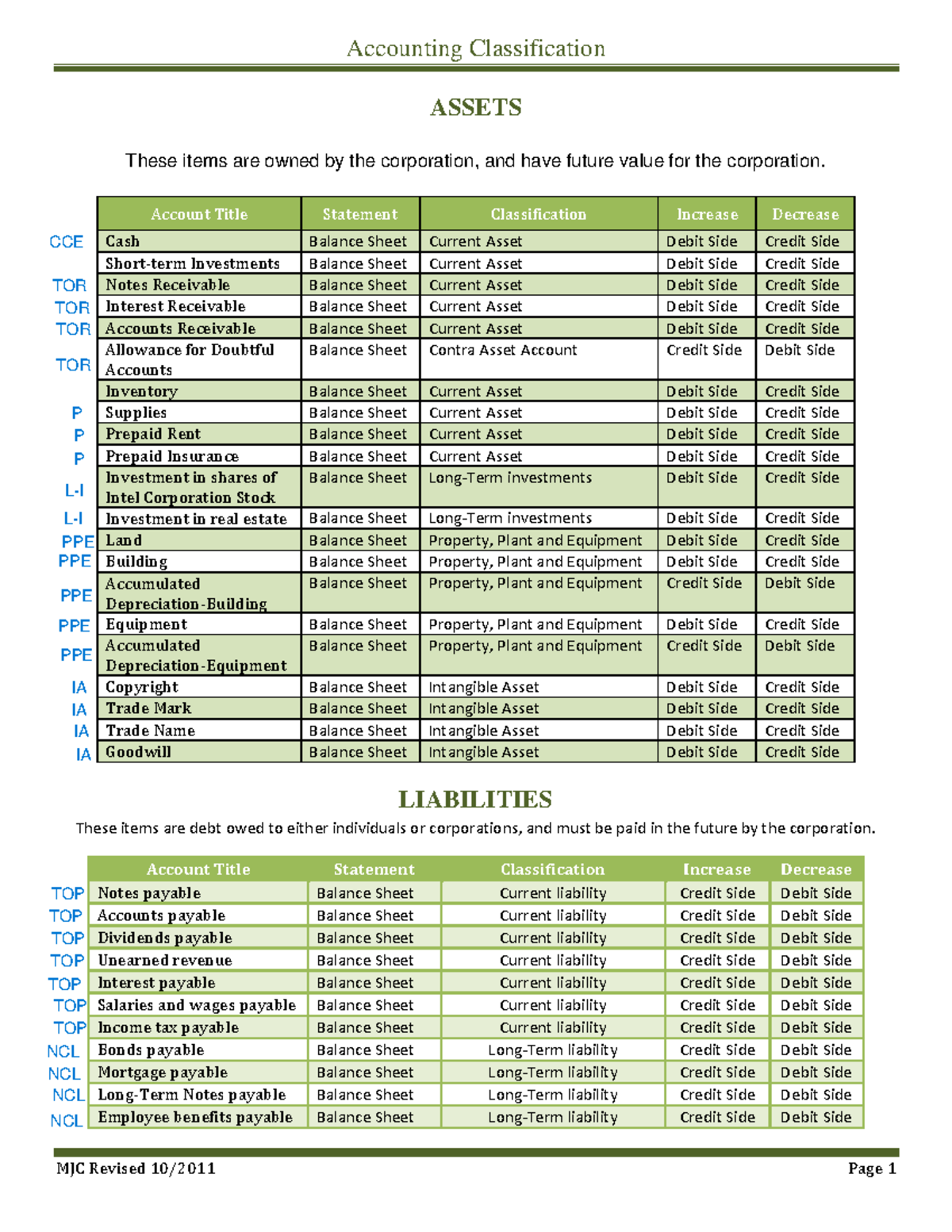
Thus, an account is an individual and a formal record of a person, firm, company, asset, liability, goods, incomes and expenses. We need to prepare one account for each type of asset, liability, income or expense. Examples of nominal accounts include sales, purchases, gains on asset sales, wages paid, and rent paid. The accounts related to real persons and organizations are classified as personal accounts. Examples of personal accounts include John’s account, Peter’s account, Procter and Gamble’s account, Vibrant Marketing Agency’s account and City bank’s account etc.
Classification of accounts makes accounting more complicated, but also more informative and detailed. Suppose you’ve bought an extensive library of computer software for the company’s computers. When you claim depreciation on the software’s loss of value due to age, all the software should depreciate at roughly the same rate. Recording all the programs in one asset classification makes it simple to apply depreciation to the whole class.
According to modern approach, the accounts are classified as asset accounts, liability accounts, capital or owner’s equity accounts, withdrawal accounts, revenue/income accounts and expense accounts. Accounting is the systematic process of recording, summarizing, and analyzing financial transactions, which is essential for businesses and individuals alike. Accounts play a crucial role in organizing these transactions, allowing for proper financial management and analysis. This article provides an overview of the various types of accounts in accounting and their significance, particularly in the Indian context. Due to its more holistic approach, the modern classification of accounts (assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses & capital) has gained more followers than the traditional classification (real, personal & nominal). Classification of accounts in the ledgers helps the accounting department create the financial statements.
The list of transactions in a particular account is called a ledger. The ledger is chronological and includes the current balance. All of the accounts taken together are called the general ledger. Pre-computer, the general ledger was an actual book with a page (actually, pages) for each account.
Personal accounts are related to the individual, debtors, or creditors. The account of John’s Capital A/c., a credit customer or the account of Harry & Co., a provider of goods, are both examples of this. The Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (or GAAP) are a set of guidelines for stimulus payments proper accounting practice. The principles include regularity, consistency, sincerity, the permanence of methods, non-compensation, prudence, continuity, periodicity, materiality, and utmost good faith. Check out our accounting category and get updates on the latest trends and insights.
